在 Spring Security(1) 这一节中已经介绍了如何用Spring Security+JWT实现认证+授权的功能,本节再做一些分析和拓展。
Spring Security默认认证的流程
在Spring Security(1)这一节中有一个helloworld的例子,它使用的是Spring Security默认的认证(登录),其流程大致如下图。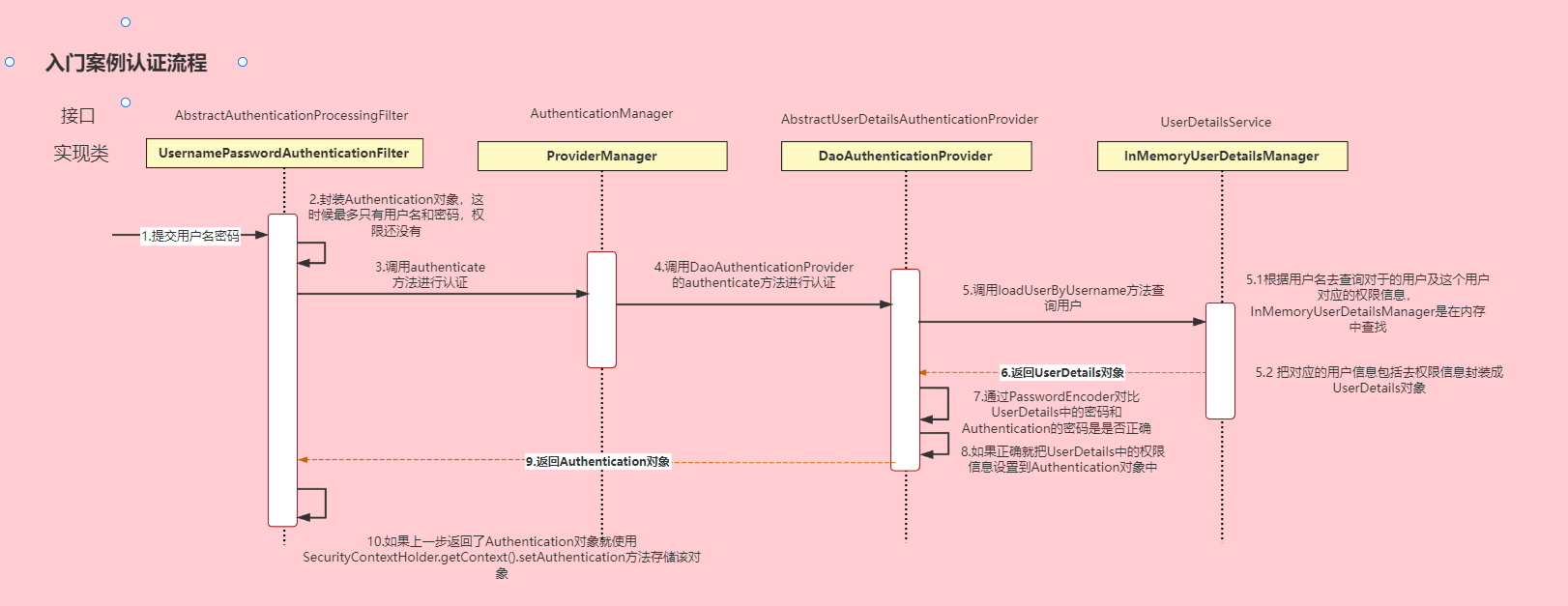
跟我们后面的自定义登录接口最大的不同点是UserDetailsService的loadUserByUsername方法,是从内存中查询的用户和权限,而不是数据库,并且内存中也只有一个用户的数据。
HttpSecruity配置接口授权
Spring Security中的权限有两种,一个是角色的,另一种就是普通的权限,通过HttpSecruity来配置的方式很灵活,一种是hasRole、hasAuthority的方法,一种是access({权限表达式})的方式。
参考如下代码。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8httpSecurity.
.antMatchers("/test1").hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/test2").access("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')")
.antMatchers("/test3").hasAnyRole("AMDIN", "USER")
.antMatchers("/test4").access("hasRole('ROLE_USER') or hasRole('ROLE_SUPER')")
.antMatchers("/test5").hasAuthority("read")
.antMatchers("/test6").access("hasAuthority('read')")
.antMatchers("/test7").hasAnyAuthority("read", "write")
Spring Security中的组件
UserDetails
UserDetails表示用户信息。它是一个接口,Spring Security中已经自带了一些实现类,但Spring Security并不是用它来做认证与授权的,而是将用户的一些信息封装在一个Authentication对象中,用这个Authentication对象来控制权限。
Authentication
Authentication 表示鉴权对象,该对象主要包含了用户的详细信息(UserDetails)和用户鉴权时所需要的信息,比如如用户提交的用户名密码、Remember-me Token,或者digest hash值等,按不同鉴权方式使用不同的Authentication实现。最常用的一个实现类就是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,它里面就包含了:
- principal:用于识别用户身份,如果使用用户名/密码方式执行的认证,这通常是一个 UserDetails 实例。
- credentials:通常是密码,在很多情况下,一旦用户通过身份认证,这部分内容便会被清除以确保不会泄露。
- authorities:GrantedAuthority 集合,是用户被授予的更高级别权限,如角色和范围。
Authentication 主要有如下两个作用:
- 作为
AuthenticationManager的输入提供用户提交的用于身份认证的凭据。在此场景下使用时isAuthenticated()方法返回 false; - 代表当前已通过身份认证的用户,可以从 SecurityContext 中获取当前的
Authentication对象。
GrantedAuthority
GrantedAuthority是一个接口,表示当前用户所拥有的的权限(或角色)信息。这些信息有授权负责对象AccessDecisionManager来使用,并决定最终用户是否可以访问某资源(URL或方法调用或域对象)。鉴权时并不会使用到该对象。
在UserDetails接口中有一个方法: Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();,用来返回用户被授予的所有权限,因为GrantedAuthority中只有一个String getAuthority();方法,所以用户的权限我们用字符串来表示就可以了。比如GrantedAuthority的其中一个实现类SimpleGrantedAuthority,它用一个role属性来权限。在比如我们用HttpSecurity用来配置授权时,也是用的‘ROLE_ADMIN’、‘read’这种字符串来表示的。
1 | public final class SimpleGrantedAuthority implements GrantedAuthority { |
而在Spring Security(1)这一节的例子中,也是通过一个set来存储系统用户的权限的。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
public class SysUser implements UserDetails {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String nickname;
private Set<GrantedAuthority> authorities;
public SysUser() {
}
public SysUser(Integer id, String username, String password, String nickname) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
/**
* 设置用户的权限
*
* @param set
*/
public void buildAuthorities(Set<String> set) {
if (set != null) {
authorities = new HashSet<>();
for (String s : set) {
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(s));
}
}
}
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return this.authorities;
}
//省略......
}
AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager(接口)是认证相关的核心接口,也是发起认证的出发点,因为在实际需求中,我们可能会允许用户使用用户名+密码登录,同时允许用户使用邮箱+密码,手机号码+密码登录,甚至,可能允许用户使用指纹登录,所以说AuthenticationManager一般不直接认证,AuthenticationManager接口的常用实现类ProviderManager内部会维护一个 ListAuthenticationManager,不同的认证方式:用户名+密码(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken),邮箱+密码,手机号码+密码登录则对应了三个AuthenticationProvider。其中有一个重要的实现类是ProviderManager。
SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder是保存安全上下文(SecurityContext)的一个容器,其原理是利用ThreadLocal在本地线程中存储数据,SecurityContext则可以用来承载GrantedAuthority,总体上如下图的关系。
如下是将授权信息保存到上下文中的代码示例:1
2
3
4
5SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
Authentication authentication = new TestingAuthenticationToken("username", "password", "ROLE_USER");
context.setAuthentication(authentication);
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context);
当然,也可以从上下文中取出用户信息与授权信息:1
2
3
4
5SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();
String username = authentication.getName();
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities();
ExceptionTranslationFilter
ExceptionTranslationFilter是Spring Security用来处理异常的过滤器。查看它的源码可以看到它主要处理了两种异常:AuthenticationException 和 AccessDeniedException。
首先看它的doFilter方法,正常不做任何处理,直接调用过滤器链的下一个过滤方法,只有出现异常的时候,会调用handleSpringSecurityException方法去处理异常。
1 | public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) |
在handleSpringSecurityException方法中对AuthenticationException 和 AccessDeniedException两种异常分别做处理,其中AccessDeniedException异常中还会判断接口是否是可以匿名访问或者有记住我(RemenberMe)的权限。
1 | private void handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request, |
AuthenticationException
对于 AuthenticationException 这种异常,它是用一个AuthenticationEntryPoint实例去处理。而这个AuthenticationEntryPoint实例是在创建ExceptionTranslationFilter对象时传进来的。
1 | private AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint; |
而AuthenticationEntryPoint的实例又是在ExceptionHandlingConfigurer类的configure方法中创建的。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42public final class ExceptionHandlingConfigurer<H extends HttpSecurityBuilder<H>> extends
AbstractHttpConfigurer<ExceptionHandlingConfigurer<H>, H> {
public void configure(H http) throws Exception {
AuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = getAuthenticationEntryPoint(http);
ExceptionTranslationFilter exceptionTranslationFilter = new ExceptionTranslationFilter(
entryPoint, getRequestCache(http));
AccessDeniedHandler deniedHandler = getAccessDeniedHandler(http);
exceptionTranslationFilter.setAccessDeniedHandler(deniedHandler);
exceptionTranslationFilter = postProcess(exceptionTranslationFilter);
http.addFilter(exceptionTranslationFilter);
}
AuthenticationEntryPoint getAuthenticationEntryPoint(H http) {
AuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = this.authenticationEntryPoint;
if (entryPoint == null) {
entryPoint = createDefaultEntryPoint(http);
}
return entryPoint;
}
private AuthenticationEntryPoint createDefaultEntryPoint(H http) { //创建默认的EntryPoint实例
if (this.defaultEntryPointMappings.isEmpty()) {
return new Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint();
}
if (this.defaultEntryPointMappings.size() == 1) {
return this.defaultEntryPointMappings.values().iterator().next();
}
DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = new DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint(
this.defaultEntryPointMappings);
entryPoint.setDefaultEntryPoint(this.defaultEntryPointMappings.values().iterator()
.next());
return entryPoint;
}
//省略......
}
最后再看代码,默认会用Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint这个类来实例化一个AuthenticationEntryPoint对象,看看Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint的源码,会向前端响应一个‘status=403,msg=Access Denied’信息。
1 | public class Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint { |
再看创建默认的EntryPoint实例的代码,如果 this.defaultEntryPointMappings.size() == 1,则会取 this.defaultEntryPointMappings.values().iterator().next() 作为默认的AuthenticationEntryPoint。也就是我们在HttpSecurity里可以自己配置一个AuthenticationEntryPoint,这样对AuthenticationException我们可以自定返回想要的数据格式,配置方式如下:1
2httpSecurity
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(new MyAuthenticationEntryPoint())
AccessDeniedException
AccessDeniedException在ExceptionTranslationFilter中则是通过一个AccessDeniedHandler对象去处理的,同样,在ExceptionHandlingConfigurer类的configure方法中可以看到默认是用AccessDeniedHandlerImpl这个实现类创建的实例。
1 | public final class ExceptionHandlingConfigurer<H extends HttpSecurityBuilder<H>> extends |
AccessDeniedHandlerImpl处理AccessDeniedException异常逻辑如下,也是会返回一个403的状态码,如果有错误页面,会转发到错误页,否则会返回‘Forbidden’的错误信息。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30public class AccessDeniedHandlerImpl implements AccessDeniedHandler {
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException,
ServletException {
if (!response.isCommitted()) {
if (errorPage != null) {
// Put exception into request scope (perhaps of use to a view)
request.setAttribute(WebAttributes.ACCESS_DENIED_403,
accessDeniedException);
// Set the 403 status code.
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value());
// forward to error page.
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(errorPage);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
}
else {
response.sendError(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value(),
HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.getReasonPhrase());
}
}
}
//省略......
}
一样的,我们也可以在HtppSecurity中配置想要的AccessDeniedHandler。1
2httpSecurity
.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(new MyAccessDeniedHandler())
EndpointRequest.toAnyEndpoint()
EndpointRequest.toAnyEndpoint()是指actuator自带的端点(endpoint),如果我们要通过Spring Security来给这些端点设置权限,可以类似如下配置,表示所有默认端点都必须有 ENDPOINT_ADMIN 的角色权限。1
2httpSecurity.requestMatcher(EndpointRequest.toAnyEndpoint()).authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().hasRole("ENDPOINT_ADMIN")
本文示例代码已上传github:https://github.com/liaosilzu2007/springsecurity-auth2-jwt。